MASH/MAFLD
Supporting your MASH/MAFLD drug development programs using a chimeric mouse model with a humanized liver.

The challenge
At PhoenixBio, we understand the complexities of building robust MASH/MAFLD drug development programs. With the disease’s many complex factors, it is challenging to discern underlying mechanisms and identify clinically significant biomarkers. Currently available animal models tend to lack key disease characteristics such as hepatocyte ballooning/fibrosis, and have lengthy timescales in presenting fibrosis after high-fat diets.
The solution
Our humanized liver chimeric mouse model enables you to overcome research and translation issues affecting the development of therapeutic agents within the growing MASH/MAFLD study fields. With two fully characterized models of diet-induced MASH, the PXB-mouse® presents the ideal model for the straightforward evaluation of drug efficacy and toxicity in a human-relevant environment. Importantly, the PXB-mouse® has a human-like lipoprotein profile, further strengthening its relevance as a MAFLD/MASH model.
Our dedicated project management teams will work with you to provide timely delivery of validated data, ensuring you receive the support you need to design and execute your MASH/MALFD drug development programs with PXB-mice.
Services Offered
- Lipid Metabolism Studies
- Cholesterol Profiling
- Bile Acid Profiling
- PK/PD Studies
- Prophylactic & Therapeutic Efficacy Treatment of Fibrosis
PXB-mice: a new translational model for MASH
Our unique chimeric PXB-mouse® with a humanized liver is a next-generation research tool that exhibits human MASH-like disease related histopathological changes including hepatocyte ballooning, mallory-denk bodies, perisinusoidal fibrogenesis, and inflammation — offering you a comprehensive validation method for pre-clinical MASH/MAFLD research studies.
The PXB-mouse® allows you to better understand the human liver condition with MASH/MAFLD, identify clinically significant biomarkers to better predict the disease and bring therapeutic agents to market.
Induce the development of MASH in as little as 12 weeks
Induce human-like MASH symptoms in PXB from 12 weeks with the choline-deficient, high-fat diet (CBAHFD), and 20-30 weeks with the Gubra-Amylin Nash (GAN) diet, closely resembling the slow onset of fibrosis caused by the ‘Western diet’ in humans.
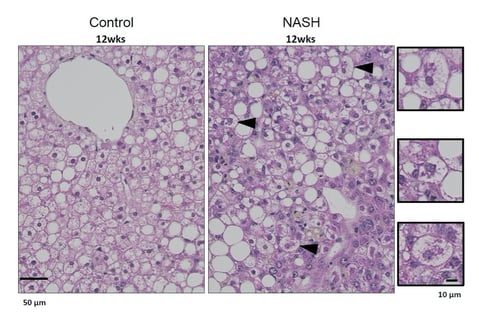
Left Panel: Control (Regular diet);
Right Panel: Choline deficient, L amino acid defined, high fat diet. H&E images at 12 weeks of diet administration. Arrows indicate hepatocyte ballooning and Mallory-Denk Bodies.
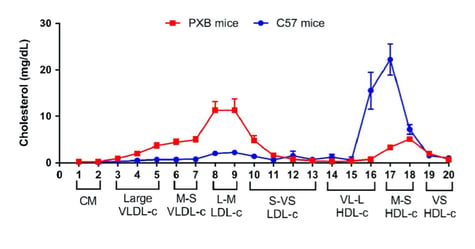
Image from: Papazyan et al., J Lipid Res. 2018 Mar 20
Test your therapeutic in a model that has a humanized lipoprotein profile
PXB-mice have a chimeric humanized liver environment containing up to 97% human hepatocytes. Their human-like lipoprotein profile makes them an ideal model to test human outcomes of MASH/MAFLD drug development programs.
Recapitulate the MASH phenotype observed in humans in our chimeric mouse model with a humanized liver. Our PXB-mice fed on a high-fat diet show human-like hepatocyte ballooning and other characteristics not typically observed in rodents.
Target fibrosis in a humanized liver chimeric mouse model
Recapitulate the MASH phenotype observed in humans in our chimeric mouse model with a humanized liver. Our PXB-mice are fed a high-fat diet show human-like hepatocyte ballooning and other characteristics not typically observed in rodents.
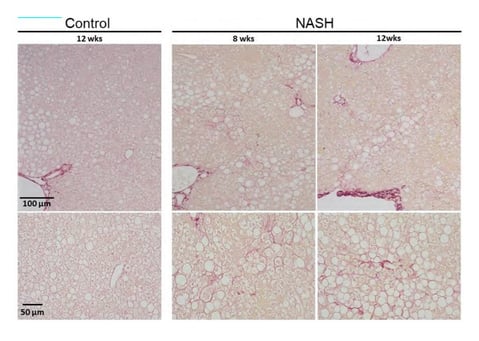
Control (Regular diet);
NASH (Choline deficient, L amino acid defined, high fat diet). Sirius Red staining images at 8-weeks and 12-weeks post diet administration. No collagen fibrils were observed in the Control group, while perisinusoidal fibrosis was observed in the NASH groups.
See how PXB-mice have been used in MASH/MAFLD studies
Our PXB-mice have helped to drive many MASH/MAFLD drug discovery projects and enabled organizations to achieve accurate human liver environment data.